LSC basics
Run modes
- There’s several run mode that you can use :
synchronous mode : this is the simplest way to start LSC. Once the source service has been listed, objects are retrieved from the source and from the destination. New objects are created, existing are updated and at the end the LSC will stop (no more daemon or program running)
clean mode : this mode is complementary to the first one for cleaning the destination service by retrieving objects and checking their existence inside the source service. If they exist nothing is done but if they don’t they are deleted from the destination service.
asynchronous mode : in this mode, LSC is started as a daemon. If the source service has something to synchronize, LSC will retrieve updated objects one by one and will synchronize it which the destination service. If no update is provided, LSC will sleep for 5 seconds and try again. It will never stop until an explicit request is done.
Phases
There are two phases:
Sync phase: LSC will add/modify/rename entries in destination
Clean phase: LSC will delete entries from destination
Sync phase
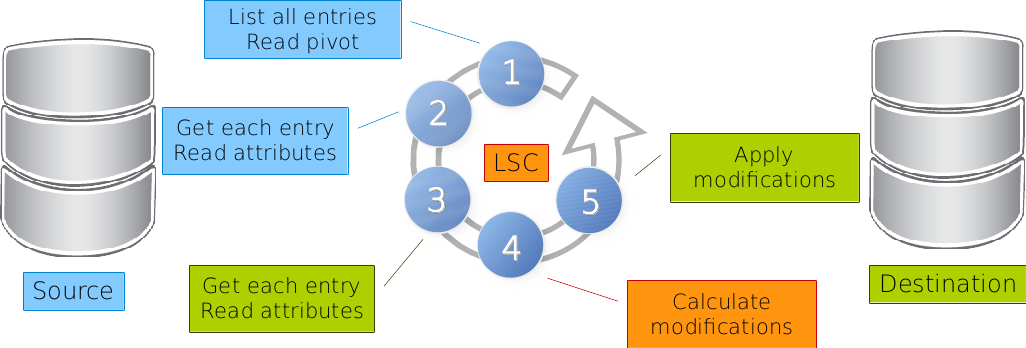
All entries are read in source. This is done with
getAllFilterfor LDAP,requestNameForListfor Database orlistScriptfor executable plugin. The values of attributes defined inpivotAttributes(in the source) are read.For each entry found at step 1, the pivot values are used to get the entry in source and values of attributes defined in
fetchedAttributesare read (in the source). This is done withgetOneFilterfor LDAP,requestNameForObjectfor Database orgetScriptfor executable plugin (in the source).For each entry found at step 1, the pivot values (from the source) are used to get the entry in destination and values of attributes defined in
fetchedAttributesare read (in the destination). This is done withgetOneFilterfor LDAP,requestNameForObjectfor Database orgetScriptfor executable plugin (in the destination).Attributes and values found at step 2 are placed in
srcBean, and those found at step 3 are indstBean. The synchronizations rules are run and LSC calculate modifications.The modification are applied on the destination, if associated
conditionsare true.
Clean phase
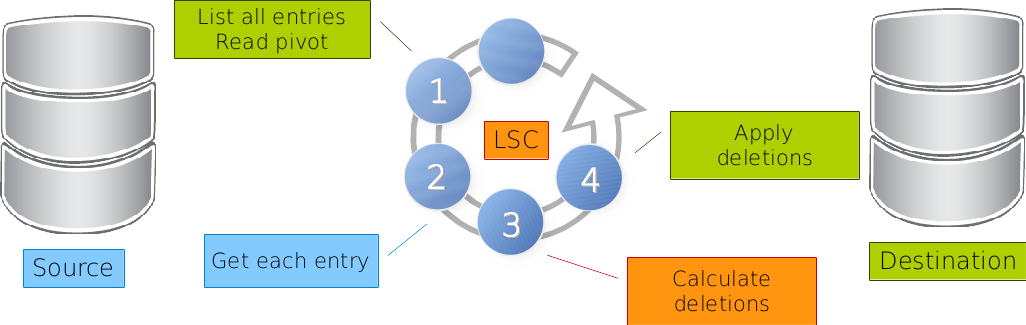
All entries are read in destination. This is done with
getAllFilterfor LDAP,requestNameForListfor Database orlistScriptfor executable plugin. The values of attributes defined inpivotAttributes(in the destination) are read.For each entry found at step 1, the pivot values (from the destination) are used to get the entry in source. This is done with
cleanFilterfor LDAP,requestNameForCleanfor Database orgetScriptfor executable plugin.If no corresponding entry is found in source, LSC tag the destination entry for deletion.
The delete are applied on the destination, if
deletecondition is true.